River system in Himachal
River System
The network of rivers formed when tributaries join the main rivers.
Tributaries
The rivers is made up of many small streams. Small streams joining big river is called tributaries.
Watershed
The high land between two drainage area.
Five rivers that run through Himachal Pradesh and supply the Indus River Basin with an abundance of water originate from the Greater Himalayas every year.
Four of the five rivers that run through Himachal Pradesh—
the Asikni (Chenab)
Purushani (Ravi)
Arjikiya (Beas)
Sutudri or Shatadru (Satluj)—are mentioned in the Rig Veda. Yamunotri gives rise to Yamuna, the fifth river.
Himachal Pradesh is a part of the extra-peninsular drainage basin. The Himachal region is unique in that it supplies water to the Ganga and Indus basins.
River system in Himachal
a) The Indus River System
The Indus River System originates in the Tibetan plateau and flows into the Himalaya in Ladakh. At around 4200 meters, it reaches the Kashmir region close to where it meets the Gurtang River.
The Naga Parbat bulk in the country’s extreme northwest and the western slopes of the Shimla ridge in Himachal Pradesh comprise the drainage basin of the Indus river system.
It encompasses the majority of Himachal Pradesh and all of Jammu and Kashmir. The Indus basin’s northernmost region includes the Cold deserts of Ladakh, Lahaul, and Pooh.
Rivers like the Satluj, Beas, Ravi, Chenab, and Jhelum are significant in this system.Out of these five, four rivers (Satluj, Beas, Ravi, Chenab) flow through Himachal Pradesh.
b) Ganga River System
This basin encompasses portions of the districts of Kinnaur, Shimla, Solan, and Sirmaur in Himachal Pradesh, as well as Garhwal, Kumaun, and Nepal.
It stretches from the eastern face of the Shimla ridge in Himachal Pradesh to the south-western slopes of the Kanchanjunga mountain on the Nepal-Sikhim border. India’s most revered river is the Ganga.
The Ganga originates close to Gangotri (Uttrakhand), beside the Gomukh glacier. The Alaknanda and Bhagirathi headstreams combine to produce the Ganga. It moves into the plains close to Haridwar.
The Yamuna meets this river near Allahahad(it was renamed as Prayagraj by UP government in october 2018) known as SANGAM. The area’s main waterway is the Ganga.
The river splits into several channels South of Farakka, creating the largest delta in the world, known as the “Sunder Ban Delta.”
The Yamuna, Bhagirathi, Alaknanda, Kali and its tributaries, the Ghagra, the Gandak, and the Kosi river are the principal tributaries of the Ganga system. The following are significant bank settlements: Patna, Varanasi, Haridwar, Kanpur, Allahabad, and Calcutta.
Table of Contents
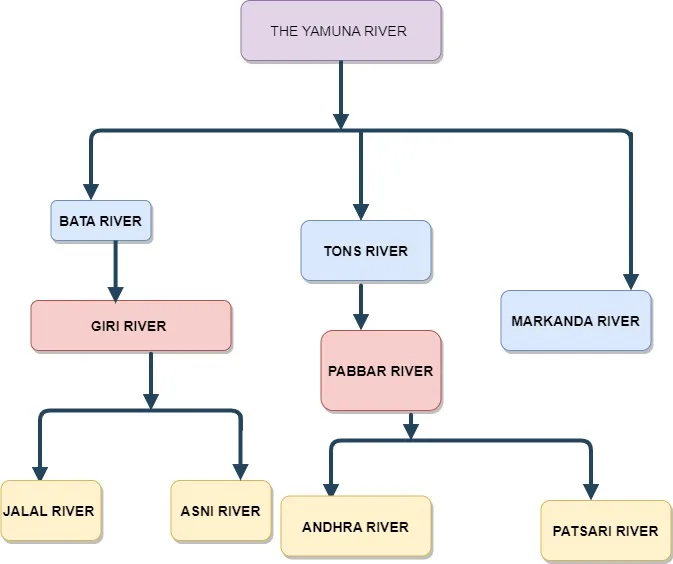
Yamuna River
It crosses into Himachal Pradesh in the Sirmaur district near “Khadar Majri.” In Himachal Pradesh, its catchment area is 2,320 square kilometers. It exits the state close to “Tajewala” and enters the state of Haryana. The course of it in Himachal Pradesh is over 22 km.The Yamuna River is the Ganga’s greatest tributary.
Note: The Sun and Yamuna have a legendary relationship.
It originates in the Garhwal Hills in “Yamunotri” and constitutes Uttarakhand’s eastern border. The Yamuna is Himachal Pradesh’s easternmost river.
Giri or Giri Ganga, Tons, and Pabbar are some of its well-known tributaries.
The Giri Ganga rises in the Shimla district just above Jubbal town, close to the “Kupar peak.”
From Yamunotri, the Tons rises.
The Pabbar from Chandra Nahan Lake close to Rohru tehsil in the Shimla district’s “Chanshal peak”
Important points:
SANSKRIT NAME: YAMUNA
VEDIC NAME: KALINDI
LOCAL NAME: JAMNA
Origin: Garhwal Hills in “Yamunotri”
Enters in Himachal near Khadar Majri,Sirmaur.
Length in himachal -22 km
Total Length:2525 Km
The Yamuna river is the smallest(length and volume wise ) river of Himachal Pradesh.
The Yamuna river is the largest tributary of Ganga River.
Click on Link: HP GK
CLICK ON LINK :HP GEOGRAPHY
YOUTUBE LINK : CLICK HERE
Tributaries of Yamuna River
Bata River
The Bata River, also known as the Jalmusa-ka-Khala, rises from the rocks beneath the “Nahan ridge” in the southwest region of Himachal Pradesh.
The following are the minor tributaries that flow into the Bata river in the Paonta valley:
A) Khara-Ka-Khaia, which originates on the Nahan Ridge and flows southward.
B) Kanser Khala, which comes from the Kanser Ridge on the Nahan’s southern slopes.
The main tributary of Bata river is Giri Ganga river.
Giri River
One significant Yamuna tributary is the Giri River. A portion of South-Eastern Himachal Pradesh is drained by it. The famed Giri, also known as Giriganga, is located in the Jubbal and Rohru hills and rises from “Kupar peak.”
It splits the Sirmaur district into two equal halves, known as the Cis-Giri and Trans-Giri area, just above Jubbal town after running through the heart of Shimla highlands in a southeasterly direction.
It then meets the Yamuna upstream of Paonta below Mokkampur. Water from the Giri River is directed into the Girinagar power house via a tunnel before entering the Bata River.
The main tributaries of Giri river is Asni River and Jalal River.
Asni River
The Asni River is the tributary of Giri Ganga River which in turns drain into Yamuna river. This river meanders through a profound valley fashioned like a V, with steep and precipitous side slopes.
Jalal River
The tiny Giri River tributary in Himachal Pradesh is called Jalal. It rises from the “Dharthi ranges,” which are next to Pacchad, and enters the Yamuna at “Dadahu,” on the right.
At Dadahu, it also merges with the Giriganga River.
This river has its source in the lower Himalayas.Dadhau and Bagthan are two of these.
Tons River
The Tons River rises from Yamunotri.This river, which enters the Yamuna at “Kalsi” in the northwest of the Dehradun valley, is a significant tributary of the latter.
It rises as the result of the following two feeder streams:
A) the Rupin River rises from a glacier at the head of the well-known Har-Ki-Dun valley, and
B) the Supin River rises in the northern portion of the Tons basin, close to the border between Himachal Pradesh and Uttrakhand.
The channel known as the Tons River flows downstream from the mountain village of “Naitwar,” where these two feeder streams come together.
The Tons River meanders through a valley formed in a V. Along the Tons River, a number of communities, including Tuni, Naitwar, and Menus, have emerged.
The river travels through the states of Haryana, Delhi, and Uttar Pradesh after passing through Himachal Pradesh before joining the Ganga in Allahabad. The total length of Yamuna river is 2,525 kilometers.
The main tributary of Tons River is Pabbar River.
Pabbar River
A tributary of the Tons River, which empties into the Yamuna River, is the Pabbar. This originates from the south-facing slopes of the Dhauladhar range between the Himachal Pradesh and Uttarakhand borders, as well as the far northeast of the Shimla district.
The Chandra Nahan glacier and springs that emerge from subterranean waters feed the main stream. At the foot of the Chakrata massif, close to the Himachal Pradesh and Uttrakhand borders, it merges with the Tons River.
Patsari River
A tiny spring-fed tributary of the Pabbar River is called the Patsari. In the Himachal Pradesh district of Shimla, this river rises from the lower Himalayan highlands close to Kharapathar.
About ten kilometres upstream of Rohru, this river merges with the Pabbar river close to the alpine village of Patsari.
Andhra river
The Pabbar River, which empties into the Tons River, is the source of this tributary. This river originates in the Shimla district, northwest of Chirgaon, from a little glacier that is tenated in a cirque of the lower Himalayan peaks.
After that, it flows generally eastward till it meets the Pabbar River near Chirgaon.
Markanda River
The Nahan area of the Sirmaur district is home to the little river Markanda. It is located at the westernmost point of the rising from the southern face of the lower Himalayas. The low undulating Shivalik hills lie on the left side of the Markanda valley, and the lower Himalayan slopes of Nahan are on the right.
हिमाचल प्रदेश में नदी तंत्र
नदी तंत्र
नदियों का नेटवर्क तब बनता है जब सहायक नदियाँ मुख्य नदियों से जुड़ती हैं।
सहायक नदियों
नदियाँ कई छोटी-छोटी जलधाराओं से मिलकर बनी होती हैं। बड़ी नदी में मिलने वाली छोटी जलधाराएँ सहायक नदियाँ कहलाती हैं।
जलविभाजन
दो जल निकासी क्षेत्रों के बीच की ऊँची भूमि।
पाँच नदियाँ जो हिमाचल प्रदेश से होकर बहती हैं और सिंधु नदी बेसिन को प्रचुर मात्रा में पानी की आपूर्ति करती हैं, हर साल ग्रेटर हिमालय से निकलती हैं।
हिमाचल प्रदेश से होकर बहने वाली पांच नदियों में से चार –
असिक्नी (चिनाब)
पुरुषानी (रावी)
अर्जिकिया (ब्यास)
और सुतुद्री या शतद्रु (सतलुज) – का उल्लेख ऋग्वेद में किया गया है। यमुनोत्री से पांचवीं नदी यमुना का उद्गम होता है।
(ए) सिंधु नदी प्रणाली
सिंधु नदी प्रणाली तिब्बती पठार से निकलती है और लद्दाख में हिमालय में बहती है। लगभग 4200 मीटर की ऊंचाई पर, यह कश्मीर क्षेत्र के करीब पहुंचती है जहां यह गुरतांग नदी से मिलती है।
देश के सुदूर उत्तरपश्चिम में नागा पर्वत का बड़ा हिस्सा और हिमाचल प्रदेश में शिमला रिज के पश्चिमी ढलानों में सिंधु नदी प्रणाली का जल निकासी बेसिन शामिल है।
इसमें हिमाचल प्रदेश का अधिकांश भाग और पूरा जम्मू-कश्मीर शामिल है। सिंधु बेसिन के सबसे उत्तरी क्षेत्र में लद्दाख, लाहौल और पूह के ठंडे रेगिस्तान शामिल हैं।
इस प्रणाली में सतलुज, ब्यास, रावी, चिनाब और झेलम जैसी नदियाँ महत्वपूर्ण हैं। इन पाँच में से, चार नदियाँ (सतलुज, ब्यास, रावी, चिनाब) हिमाचल प्रदेश से होकर बहती है।
(बी) गंगा नदी प्रणाली
यह बेसिन हिमाचल प्रदेश के किन्नौर, शिमला, सोलन और सिरमौर जिलों के साथ-साथ गढ़वाल, कुमाऊं और नेपाल के कुछ हिस्सों को कवर करता है।
यह हिमाचल प्रदेश में शिमला रिज के पूर्वी हिस्से से लेकर नेपाल-सिखिम सीमा पर कंचनजंगा पर्वत के दक्षिण-पश्चिमी ढलान तक फैला हुआ है। भारत की सबसे पूजनीय नदी गंगा है।
गंगा का उद्गम गंगोत्री (उत्तराखंड) के निकट, गोमुख ग्लेशियर के बगल से होता है। अलकनंदा और भागीरथी की मुख्य धाराएँ मिलकर गंगा का निर्माण करती हैं। यह हरिद्वार के करीब मैदानी इलाकों में चला जाता है। यमुना इस नदी से अल्लाहहाद के पास मिलती है (अक्टूबर 2018 में यूपी सरकार ने इसका नाम बदलकर प्रयागराज कर दिया था) जिसे संगम के नाम से जाना जाता है। क्षेत्र का मुख्य जलमार्ग गंगा है।
नदी फरक्का के दक्षिण में कई चैनलों में विभाजित हो जाती है, जिससे दुनिया का सबसे बड़ा डेल्टा बनता है, जिसे “सुंदर बन डेल्टा” के नाम से जाना जाता है। यमुना, भागीरथी, अलकनंदा, काली और उसकी सहायक नदियाँ, घाघरा, गंडक और कोसी नदी गंगा प्रणाली की प्रमुख सहायक नदियाँ हैं। निम्नलिखित महत्वपूर्ण बैंक बस्तियाँ हैं: पटना, वाराणसी, हरिद्वार, कानपुर, इलाहाबाद और कलकत्ता।
यमुना नदी
यह “खादर माजरी” के पास सिरमौर जिले में हिमाचल प्रदेश में प्रवेश करती है। हिमाचल प्रदेश में इसका जलग्रहण क्षेत्र 2,320 वर्ग किलोमीटर है।
यह “ताजेवाला” के निकट राज्य से बाहर निकलती है और हरियाणा राज्य में प्रवेश करती है। हिमाचल प्रदेश में इसका मार्ग 22 किमी है। यमुना नदी गंगा की सबसे बड़ी सहायक नदी है।
नोट: सूर्य और यमुना का पौराणिक संबंध है।
इसका उद्गम “यमुनोत्री” में गढ़वाल की पहाड़ियों से होता है और यह उत्तराखंड की पूर्वी सीमा बनाती है। यमुना हिमाचल प्रदेश की सबसे पूर्वी नदी है।
गिरि या गिरि गंगा, टोंस और पब्बर इसकी कुछ प्रसिद्ध सहायक नदियाँ हैं।
गिरि गंगा शिमला जिले में जुब्बल शहर के ठीक ऊपर, “कुपर शिखर” के करीब से निकलती है।
यमुनोत्री से टोंस निकलती है।
शिमला जिले के “चांशल शिखर” में रोहड़ू तहसील के करीब चंद्र नाहन झील से पब्बर निकलती है।
महत्वपूर्ण बिंदु:
संस्कृत नाम: यमुना
वैदिक नाम: कालिंदी
स्थानीय नाम: जमना
उद्गम स्थल: “यमुनोत्री” में गढ़वाल की पहाड़ियाँ
खादर माजरी, सिरमौर के पास हिमाचल में प्रवेश करती है।
हिमाचल में लंबाई -22 किमी
कुल लंबाई: 2525 किमी
यमुना नदी हिमाचल प्रदेश की सबसे छोटी (लंबाई और आयतन के अनुसार) नदी है।
यमुना नदी गंगा नदी की सबसे बड़ी सहायक नदी है।
यमुना नदी की सहायक नदियाँ
बाटा नदी
बाटा नदी, जिसे जलमुसा-का-खाला के नाम से भी जाना जाता है, हिमाचल प्रदेश के दक्षिण-पश्चिम क्षेत्र में “नाहन रिज” के नीचे चट्टानों से निकलती है। पोंटा घाटी में बाटा नदी में बहने वाली छोटी सहायक नदियाँ निम्नलिखित हैं:
ए) खरा-का-खिया, जो नाहन रिज से निकलती है और दक्षिण की ओर बहती है।
बी) कांसेर खाला, जो नाहन के दक्षिणी ढलान पर कांसेर रिज से निकलती है।
बाता नदी की मुख्य सहायक नदी गिरि गंगा नदी है।
गिरि नदी
यमुना की एक महत्वपूर्ण सहायक नदी गिरि नदी है। दक्षिण-पूर्वी हिमाचल प्रदेश का एक भाग इससे प्रवाहित होता है। प्रसिद्ध गिरि, जिसे गिरिगंगा के नाम से भी जाना जाता है, जुब्बल और रोहड़ू पहाड़ियों में स्थित है और “कुपर शिखर” से निकलती है।
यह सिरमौर जिले को दो बराबर हिस्सों में विभाजित करता है, जिन्हें सिस-गिरि और ट्रांस-गिरि क्षेत्र के रूप में जाना जाता है, जो दक्षिण-पूर्व दिशा में शिमला के ऊंचे इलाकों के बीचों-बीच चलने के बाद जुब्बल शहर के ठीक ऊपर है। फिर यह मोक्कमपुर के नीचे पांवटा की ऊपरी धारा में यमुना से मिलती है
गिरि नदी का पानी बाटा नदी में प्रवेश करने से पहले एक सुरंग के माध्यम से गिरिनगर बिजली घर में निर्देशित किया जाता है।
असनी नदी और जलाल नदी ,गिरि नदी की मुख्य सहायक नदियाँ हैं।
असनी नदी
असनी नदी गिरि गंगा नदी की सहायक नदी है जो आगे चलकर यमुना नदी में मिल जाती है। यह नदी वी के आकार की एक गहरी घाटी से होकर बहती है, जिसके पार्श्व ढलान तीव्र हैं।
जलाल नदी
हिमाचल प्रदेश में गिरी नदी की छोटी सहायक नदी को जलाल कहा जाता है। यह “धरथी पर्वतमाला” से निकलती है, जो पच्छाद के बगल में है, और दाईं ओर “ददाहू” में यमुना में प्रवेश करती है।
ददाहू में यह गिरिगंगा नदी में भी मिल जाती है। इस नदी का उद्गम निचले हिमालय में है। दधौ और बागथन इनमें से दो हैं।
टोंस नदी
टोंस नदी यमुनोत्री से निकलती है। यह नदी, जो देहरादून घाटी के उत्तर-पश्चिम में “कलसी” में यमुना में प्रवेश करती है। यह निम्नलिखित दो फीडर धाराओं के परिणामस्वरूप निकलती है: रूपिन नदी प्रसिद्ध हर-की-दून घाटी के शीर्ष पर एक ग्लेशियर से निकलती है, और सुपिन नदी टोंस बेसिन के उत्तरी भाग में, के करीब से निकलती है।
टोंस नदी के रूप में जाना जाने वाला चैनल “नैटवार” के पहाड़ी गांव से नीचे की ओर बहता है, जहां ये दो फीडर धाराएं एक साथ आती हैं। टोंस नदी वी में बनी एक घाटी से होकर बहती है। टोंस नदी के किनारे, ट्यूनी, नैटवार और मेनस सहित कई समुदाय उभरे हैं।
यह नदी इलाहाबाद में गंगा में मिलने से पहले हिमाचल प्रदेश से गुजरने के बाद हरियाणा, दिल्ली और उत्तर प्रदेश राज्यों से होकर गुजरती है। यमुना नदी की कुल लम्बाई 2,525 किलोमीटर है।
टोंस नदी की मुख्य सहायक नदी पब्बर नदी है।
पब्बर नदी
टोंस नदी की एक सहायक नदी पब्बर है, जो यमुना नदी में गिरती है। इसका उद्गम हिमाचल प्रदेश और उत्तराखंड सीमाओं के बीच धौलाधार पर्वत श्रृंखला के दक्षिण की ओर ढलानों के साथ-साथ शिमला जिले के सुदूर उत्तर-पूर्व से होता है।
चंद्र नाहन ग्लेशियर और भूमिगत जल से निकलने वाले झरने मुख्य धारा को पोषण देते हैं। हिमाचल प्रदेश और उत्तराखंड की सीमाओं के करीब, चकराता पर्वत की तलहटी में, यह टोंस नदी में विलीन हो जाती है।
पटसारी नदी
पब्बर नदी की एक छोटी झरने वाली सहायक नदी को पटसारी कहा जाता है। हिमाचल प्रदेश के शिमला जिले में, यह नदी खड़ापत्थर के करीब निचले हिमालयी ऊंचे इलाकों से निकलती है। रोहड़ू से लगभग दस किलोमीटर ऊपर, यह नदी पटसारी के अल्पाइन गांव के पास पब्बर नदी में विलीन हो जाती है।
आंध्रा नदी
पब्बर नदी, जो टोंस नदी में गिरती है, इस सहायक नदी का स्रोत है। यह नदी शिमला जिले में, चिरगांव के उत्तर-पश्चिम में, एक छोटे ग्लेशियर से निकलती है जो निचली हिमालय की चोटियों के एक घेरे में स्थित है। उसके बाद, यह आम तौर पर पूर्व की ओर बहती है जब तक कि यह चिरगांव के पास पब्बर नदी से नहीं मिल जाती।
मारकंडा नदी
सिरमौर जिले का नाहन क्षेत्र छोटी नदी मारकंडा का घर है। यह निचले हिमालय के दक्षिणी भाग से निकलने के सबसे पश्चिमी बिंदु पर स्थित है। मार्कंडा घाटी के बाईं ओर निचली लहरदार शिवालिक पहाड़ियाँ हैं, और दाहिनी ओर नाहन की निचली हिमालयी ढलानें हैं।






Leave a Comment