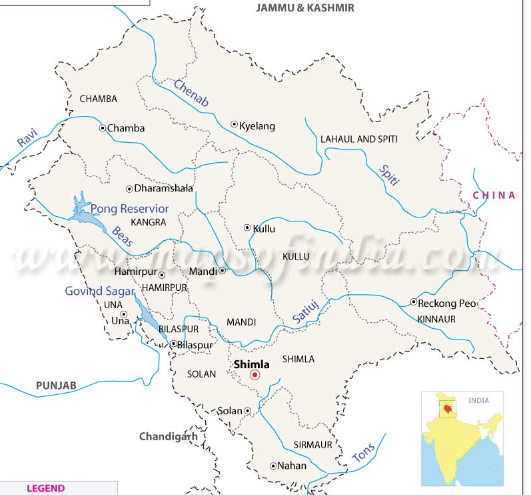
Chenab river and Tributaries in english
Let us discuss about Chenab river and Tributaries in detail
Chenab river
IMPORTANT POINTS:
- Origin – Baralacha pass
- Chenab river is also known as ChandarBhaga(Chandra means Rangoli in lahul local language and Bhaga means Gara in lahul local language )
- Two main tributaries of chenab : Chandar river and Bhaga river
- Chandar river rises from South-east of Baralacha pass.
- Bhaga river rises from North-West of Baralacha pass.
- Chandar river and Bhaga river merge at Tandi, Lahul.
- Length in HP – 120 KM
- Total Length – 1200Km
- Chenab is the largest river of Himachal Pradesh in terms of water volume.
- Vedic Name: Askini
- Greek Name: Akesines
The river Chenab is formed by the meeting of two streams, Chandra and Bhaga, near Tandi, 2,280 metres above sea level. The streams originate on opposing sides of the Baralacha pass at 4,891 metres above sea level. North-West of the Baralacha Pass is where the Bhaga and Chandra rise.
It exits the district at “Sansari Nala” to enter the Podar valley of Kashmir after entering the Pangi valley in the Chamba district close to “Bhujind.” It flows 122 kilometres through Himachal. Its catchment area, which spans 1,200 km, is 61,000 sq km, of which 7,509 sq km are located in Himachal Pradesh. Given the volume of water in it, this is Himachal Pradesh’s largest river.The enormous Himalayan and Pir Panjal ranges generated a structural dip that is known as the Chenab valley.
Chenab river Tributaries
Let us discuss about Chenab river Tributaries in detail
Miyar Nallah
While the Saicher Nallah enters Chenab in the Pangi Valley, the Miyar Nallah does so in Lahaul. The rivers Jammu Tavi and Bhaga are its tributaries in its lower course, and the river Munawarwali is located in the Dun valley. It eventually joins the Arabian Sea after meeting the Indus River at Mithankot, approximately 950 miles downriver in Pakistan. Along this river, some significant human towns have emerged, including Udaipur, Killar, Doda, and Ramban.
Bhaga River
This river rises in the valley of Lahaul. It flows via several snowfed rivers before joining the Chandra stream in Tandi. Before it joins the Chandra River, it rushes fiercely in a south-southwest direction from its source. The upper basin of the Bhaga river is characterised by u-shaped valleys, waterfalls, glaciers, and moraines. There isn’t any vegetation covering the entire stretch. When the snow on the high mountains begins to melt in the summer, this river’s discharge increases.
Chandra River
In the Lahaul-Spiti district, it rises in the snow at the foot of the main Himalayan range. After then, it runs southeast along the base of the narrow range for a considerable distance before turning about and travelling southwest through the Spiti Valley. Because it is located in the rain shadow of the Pir Panjal range, which is oriented towards the south, the entire region is a huge, freezing desert with little to no rainfall. Koksar is a significant human community along the river.
Other tributaries of Chenab:
- Tavi river
- yoch nala
- milang

Click on Link: HP GK
CLICK ON LINK :HP GEOGRAPHY
चिनाब नदी और सहायक नदियाँ
चिनाब नदी
महत्वपूर्ण बिंदु:
- उद्गम स्थल – बारालाचा दर्रा
चिनाब नदी को चंद्रभागा के नाम से भी जाना जाता है (लाहुल की स्थानीय भाषा में चंद्र का अर्थ है रंगोली और लाहुल की स्थानीय भाषा में भाग का अर्थ है गारा)
चिनाब की दो मुख्य सहायक नदियाँ: चंदर नदी और भागा नदी
चंदर नदी बारालाचा दर्रे के दक्षिण-पूर्व से निकलती है।
भागा नदी बारालाचा दर्रे के उत्तर-पश्चिम से निकलती है।
चंदर नदी और भागा नदी तांदी, लाहुल में विलीन हो जाती है।
एचपी में लंबाई – 120 किमी
कुल लंबाई – 1200 किमी
जल की मात्रा की दृष्टि से चिनाब हिमाचल प्रदेश की सबसे बड़ी नदी है।
वैदिक नाम: अस्किनी
यूनानी नाम: अकेसिनेस
चिनाब नदी समुद्र तल से 2,280 मीटर ऊपर तांदी के पास दो धाराओं, चंद्रा और भागा के मिलने से बनती है। जलधाराएँ समुद्र तल से 4,891 मीटर ऊपर बारालाचा दर्रे के विपरीत किनारों से निकलती हैं। बारालाचा दर्रे के उत्तर-पश्चिम में भागा और चंद्रा का उदय होता है।
यह “संसारी नाला” पर जिले से बाहर निकलकर “भुजिंद” के करीब चंबा जिले में पांगी घाटी में प्रवेश करने के बाद कश्मीर की पोदार घाटी में प्रवेश करती है। यह हिमाचल में 122 किलोमीटर बहती है। इसका जलग्रहण क्षेत्र, जो 1,200 किमी तक फैला है, 61,000 वर्ग किमी है, जिसमें से 7,509 वर्ग किमी हिमाचल प्रदेश में स्थित है। इसमें पानी की मात्रा को देखते हुए, यह हिमाचल प्रदेश की सबसे बड़ी नदी है। विशाल हिमालय और पीर पंजाल पर्वतमाला ने एक संरचनात्मक गिरावट उत्पन्न की जिसे चिनाब घाटी के रूप में जाना जाता है।
चिनाब नदी की सहायक नदियाँ
मियार नाला
सैचर नाला पांगी घाटी में चिनाब में प्रवेश करता है, मियार नाला लाहौल में चिनाब में प्रवेश करता है है। जम्मू तवी और भागा नदियाँ इसके निचले प्रवाह में इसकी सहायक नदियाँ हैं, और मुनावरवाली नदी दून घाटी में स्थित है। यह अंततः पाकिस्तान में लगभग 950 मील नीचे मिथनकोट में सिंधु नदी से मिलने के बाद अरब सागर में मिल जाती है। इस नदी के किनारे, कुछ महत्वपूर्ण मानव शहर उभरे हैं, जिनमें उदयपुर, किलाड़, डोडा और रामबन शामिल हैं।
भागा नदी
यह नदी लाहौल की घाटी से निकलती है। तांदी में चंद्रा धारा में शामिल होने से पहले यह कई बर्फीली नदियों से होकर बहती है। चंद्रा नदी में शामिल होने से पहले, यह अपने स्रोत से दक्षिण-दक्षिणपश्चिम दिशा में तीव्र गति से बहती है। भागा नदी के ऊपरी बेसिन की विशेषता यू-आकार की घाटियाँ, झरने, ग्लेशियर और मोराइन हैं। पूरे क्षेत्र में कोई भी वनस्पति नहीं है। गर्मियों में जब ऊंचे पहाड़ों पर बर्फ पिघलने लगती है तो इस नदी का बहाव बढ़ जाता है।
चंद्रा नदी
लाहौल-स्पीति जिले में, यह मुख्य हिमालय श्रृंखला की तलहटी में बर्फ से उगता है। उसके बाद, यह स्पीति घाटी के माध्यम से दक्षिणपश्चिम की ओर मुड़ने और यात्रा करने से पहले काफी दूरी तक संकीर्ण सीमा के आधार के साथ दक्षिण-पूर्व की ओर चलती है। चूँकि यह पीर पंजाल पर्वतमाला की वर्षा छाया में स्थित है, जो दक्षिण की ओर उन्मुख है, पूरा क्षेत्र एक विशाल, जमा देने वाला रेगिस्तान है जहाँ बहुत कम या कोई वर्षा नहीं होती है। कोकसर नदी के किनारे एक महत्वपूर्ण मानव समुदाय है।
- चिनाब की अन्य सहायक नदियाँ:
- तवी नदी
- योच नाला
- मिलांग